|

BlackDiamond 12804C Series
|
오늘날의
기업네트워크는 집중형이 계속되며, 네트워크의 중앙과
집합레이어에서 application-level 인식을 위한 증가되는
필요성에 기반한다.
집중네트워크의
리더로써, Extreme Networks® 은 BlackDiamond 12804C
스위치로 이더넷 네트워킹을 위한 새로운 수준의 지능을
제공한다.
BlackDiamond
12804C는, BlackDiamond 10808 같이 프로그램이 가능한
ASIC technology 통합한다.
이
프로그램
능력은 플랫폼이 비용적인 하드웨어 업그레이드 없이 새로운
프로토콜을 지원할것을 확신한다.
|
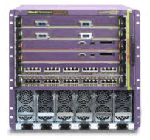
|
BlackDiamond
12804C 는 고수행, 확장성과 높은수준의 탄력성을 필요로 하는 중앙이나
집합 어플리케이션에 이상적이다.
더욱
중요한것은, BlackDiamond 12804C 는 현재뿐만 아니라 차세대의 필요성을
충족시켜주기 위해 설계되었다.
확장성은
변화하는 요구사항을 지원과 응대할수 있는 지능적인 중앙 네트워크를
설계하기위한 핵심이다.
Target
Applications
BlackDiamond
12804C 는 어플리케이션의 다양한 배치에 우수하도록 설계되었다.
- 중·소기업을
위한 핵심 어플리케이션
- 보안환경을
위한 전통적인 기가비트나 10기가비트 이더넷 집합스위치
어플리케이션
수행을 강화하기위한 설계
- QoS와
어플리케이션 확장성을 제공하는 수행
- multicast(다수전송)
어플리케이션을 위한 시스템 확장성
- 이더넷
자동방어 스위칭(EAPS) 을 이용하는 고이용성 네트워크
Voice-Class
Availability
- 충분한
hardware design
- ExtremeXOS™
modular operating system
- 이더넷
자동방어 스위칭(EAPS) 을 이용하는 고이용성 네트워크
Resiliency
Under Attack(네트워크 공격에 대한 탄력성)
- CLEAR-Flow
Security Rules Engine 으로 침입탐지와 응대
- 고객도메인을
분리하기위한 Layer 3 Virtual Switching
- 강화된
네트워크 인프라
Designed
to Enforce Application Performance
BlackDiamond
12804C 는 어떤기능이 사용되던간에 독립적인 deterministic 수행을
제공한다.
Application
Scalability(확장성)
QoS
Performance
BlackDiamond
12804C 는 architecture 전체에 deep packet buffer 를 전달하며, 혼잡시간에서
조차도 패킷은 대기될수 있으며
신뢰성있게
전달된다.
반면에
이러한 혼잡시간 동안에 대기시간이 증가되면, 저급 스위치는 초과되는
트래픽을 버릴것이다.
트래픽
buffering 으로 인해, 서버는 네트워크와 컴퓨터엔진 양쪽의 효율성
증가로 끊김과 극대로 증가하는 트래픽을 재전송할 필요가 없다.
Low
Latency(낮은 대기시간)
집합어플리케이션을
위한 네트워크 스위치를 선택할때,
네트워킹
컴포넌트를 위하여 낮은 대기시간을 선택하는것은 다른요소에 의해 발생한
작업대기시간을 위한 여분추가를 제공한다.
64-byte
패킷을 위한 9 microsecond 의 낮은 스위칭 대기시간으로, BlackDiamond
12804C 는 집합어플리케이션에 이상적이다.
Jumbo
Frame Support
9,216
byte 의 Jumbo frame 은 BlackDiamond 12804C 에 의해서 지원된다.
Jumbo
frame 은 고수행 cluster computing application 에서 특별히 중요하며,
연구결과에 의하면 이들의 이용은
서버부담을
50% 만큼이나 줄여줄수있다.
Jumbo
frame 은 또한 프로토콜 overhead 를 줄여주며 protocol header 가 고정된
크기가 된후로 높은 전체네트워크 처리량을 확신하며,
커다란
frame 은 packet header 를 향한 packet payload 의 높은비율을 가진다.
Multicast
BlackDiamond
12804C 는 하드웨어 인증과 multicast traffic 의 replication 지원으로,
IP multicast 에서 Extreme Networks'
leadership position 을 가져다주었다.
Extreme
Networks unique switch fabric architecture 는 fabric 을 가로지르는
같은 패킷의 다수저장과 전송이 필요치 않다.
이것은
스위치를 통하는 다른 운영중인 트래픽에 영향을 주지않고 뛰어난 multicast
수행을 확신한다.
Multicast
특징은 인터넷그룹 관리 프로토콜(IGMPv2 & v3) 과 프로토콜 독립
Multicast (PIM)를 포함한다.
양쪽다
Sparse Mode 와 Dense Mode PIM 이 지원된다.
Scalable
Management Through Extensibility
Ease
of Management
Extreme
네트워크는 네트워크를 다루는데 있어서 시간과 리소스를 절약해주는
발달된 tool 을 가지고있다.
EPICenter®
는 집합네트워크에서 Extreme Networks' multi-layer switching 장비를
다루기위해 all fault configuration
(무정지형 환경설정), accounting,
performance, security 기능을 제공한다.
EPICenter
Policy Manager 는 Layer 1-4 를 위한 레이어 독립정책 시행을 제공한다.
Extreme
의 software application, ServiceWatch® 는 강력한 Layers 4-7
monitoring 과 mission-critical 네트워크 서비스를 위한 관리를
전달한다.
Extensibility
to Integrate New Applications
ExtremeXOS
는 OS시스템과 직접적으로 상호작용을 위한 네트워크에서 third-party
어플리케이션을 위한 mechanism 제공함 으로써
네트워크 능력의 융통성있는
확장을 허용한다.
ExtremeXOS
는 best-of-breed monitoring 과 보안장비와 상호작용을 위해서 secure
XML-based API 를 이용한다.
이
확장성은 새로운 모니터링과 반응능력을 위한 closed loop 을 제공하기
위해 third-party 어플리케이션과 상호작용을 허용한다.
(Figure 1 참고)
Converged
Network Analyzer
Extreme
네트워크의 집합네트워크 분석스위치(Analyzer Switch) 는 LAN상에서
고품질 QoS를 제공한다.
Avaya®
의 집합네트워크 분석기는 (CNA) WAN 상에서 QoS 를 최적화 하기위한
능력으로 Extreme Networks LAN advantage 를
향상시기기 위한 능력을
제공한다. Extreme
네트워크 인프라와 결합된 CNA 와 LAN상의 QoS 는 Voice-over-IP (VoIP)
와 다른
business-critical 어플리케이션을 위한 최적화된 end-to-end
IP 네트워크를 제공한다.
Extreme
네트워크는 ExtremeXOS 기반 스위치에서 Avaya’s CNA monitoring software 를 내장하고있다.
CNA
는 IP WAN 네트워크 상에서 상반되는 어플리케이션 수행으로 addressing
issue 에 의해 네트워크를 좀더 신뢰성있게 만든다.
CNA
소프트웨어는 기존에 알려진것과 다른 어플리케이션에 영향을주는 문제들을
위하여 IP 네트워크를 감시한다.
optional
Adaptive Path Controller module 은 하나가 이용가능할때 언제라도
좀더나은 수행을 선택함에 의해 네트워크 상에서 문제점을
적극적으로
피하기
위해 이들 평가결과(assessment result) 를 이용한다.
Voice-Class
Availability
고성능
네트워크 접속으로, 대규모로 PCs ,IP telephone 서버에 상관없이 이용하는데
매우 유용하다.
BlackDiamond
12804C 는 스위치 서비스 중단없이 OS 업그레이드가 가능하다.
BlackDiamond
ExtremeXOS 는 Extreme 네트워크의 industry-leading 모듈러 OS이며,
Network
level 탄력적인 프로토콜이 네트워크 이용성을 증가시키기 위해 추가되었다.
Redundant
Hardware Design
Fully
Redundant Management Modules (1:1)
BlackDiamond
12804C 는 hitless failover(대체작동) mechanism 으로 구성되어있다.
관리스위치
모듈(MSM) 오류시에, second MSM 이 전체 스위치를 위해 자동으로 관리와
스위칭 책임을 인수받을 것이다.
이특징은
운영중인 음성과 다른 mission-critical 어플리케이션 네트워크에 필수적이다.
Advanced
Chassis Design for Availability
BlackDiamond
12804C 는 고립된 제어와 data plane, 파워분배를 위한 redundant controller
board, 네트워크 이용성에 영향을 주는
악의적 요소를 식별하기
위한
환경모니터링과 같은 고이용성 설계 요소로 인해 상호 보완되는 backplane
을 포함한다.
Redundant
Load Sharing Power Supplies
BlackDiamond
12804C 는 동시에 6개 까지의 내부 파워서플라이를 공유해서 적재할수
있는 충분한 파워 환경설정을 지원한다.
이들
파워서플라이는 파워서플라이 중복(redundancy)을 위해 N + 1 환결성정이나
모두 적재된 샤시를 위한 파워중복(redundancy)을
제공하기위해 N
+ N 환경설정으로 구성될수 있다.
Modular
Operating System for Non-stop Operations
Hitless
Software Upgrade
BlackDiamond
12804C 는 hitless 소프트웨어 업그레이드를 지원하며, 관리윈도우나 스위치
중단없이 스위치 업그레이드를 허용한다.
이것은
네트워크 가동시간을 증가시키며 네트워크 사용중단 없이 새로운 소프트웨어
특징의 이점을 취하는것을 허용한다.
True
Preemptive Multitasking and Protected Memory
ExtremeXOS
는 Figure 2 에서 보여주는 것처럼 각기 다른것으로부터 보호되는 분리된
OS 에서 운영하기 위한 OSPF 와 스패닝트리 같은
각기 다른작업을 허용한다.
Process
Monitoring and Restart
ExtremeXOS
는 실시간으로 독립적인 OS 처리 모니터링으로 네트워크 이용성을 극도로
향상시킨다.
만약
이중 하나라도 응답이 없거나 운영이 중지된다면, 자동으로 재시작된다.
Loadable
Software Modules
ExtremeXOS
의 모듈러 설계는 새로운 OS 이미지 로딩과 스위치 재시작없이 기능적인
스위치 확장을 허용한다.
새로운
기능성은 운영중인 스위치에 추가될수있다.
High
Availability Network Protocols
Ethernet
Automatic Protection Switching
EAPS
는 IP network 에 탄력성과 유저들이 전통적인 음성 네트워크로 부터
기대하는 가동시간을 제공한다.
EAPS
는 Spanning Tree 나 Rapid Spanning Tree 보다 우수하며,
sub-second (50 milliseconds 보다 적은) 회복을 제공한다.
대부분의
상황에서, EAPS 는 네트워크가 링크 오류로부터 거의 투명하게 회복되는것을
가능하게 하기 때문에 VoIP call 은 떨어지지
않으며 디지털
비디오 공급은 동결되거나 pixelize 가 되지않는다.
Spanning
Tree/Rapid Spanning Tree Protocols
BlackDiamond
12804C 는 Layer 2 탄력성을 위한 Spanning Tree, VLAN Spanning Tree
(802.1D), Rapid Spanning Tree (802.1w)
프로토콜을 지원한다.
Software
Enhanced Availability
Software
Enhanced Availability 는 네트워크 인프라중 부분이 다운되었을때 조차도
유저들이 네트워크에 연결된 상테로 남아있게 해준다.
ExtremeXOS
는 OSPF ,VRRP ,ESRP (Layer 2 나 Layer 3 에서 지원되는 ESRP)
와 같은 진보된 Layer 3 프로토콜을 이용하여
네트워크
연결 문제점을 꾸준히 체크한다.
Equal
Cost Multipath
Equal
Cost Multipath 는 링크가 로드밸런스 되게하며 충분한 대체작동을 지원하는
동안에 비용절감이 가능하게한다.
링크
오류시에는, 트래픽은 자동으로 남아있는 링크로 전환되며 연결상태로
남게된다.
Link
Aggregation (802.3ad)
Cross
module link aggregation 은 단일지역 연결에서 8개 까지의 trunking
을 가능하게 하며, 지역연결 마다 충분한 대역폭인 80 Gbps
까지 가능하게한다.
Resiliency
Under Attack
BlackDiamond
12804C 는 Ethernet core networking 을 위한 새로운 레벨의 보안을
전달한다.
BlackDiamond
12804C 는 현재 보호되지 않는 네트워크의 soft interior 보호에 의해서
perimeter firewall 을 보완한다.
가장진보된
CLEAR-Flow Security Rules Engine 을 이용함 으로써, 자동탐지가 프로그램
될수있으며 단시간내에 보안위협을 경감시킨다.
Threat
Detection and Response
CLEAR-Flow
Security Rules Engine
CLEAR-Flow
Security Rules Engine 은 first order 침입탐지와 경감 그리고 네트워크
상에서 의심스러운 트래픽의 더나은 분석을 위한
가상화된 보안
리소스(VSRs) 를 위한 mirror traffic 을 제공한다.
VSRs
는 전체 multi-gigabit 네트워크를 통하여 가상으로 이용가능하다. 그러므로
보안 솔루션의 비용절감적인 확장성을 가능하게한다.
예를들어,
Extreme 네트워크의 Sentriant™ VSR 은 BlackDiamond 12804C 스위치의
CLEARFlow rule 과 추가되는 트래픽을 감시하거나
검사 시점을 변경하기
위한 Access Control List(ALCs)의 추가/수정이 가능하다. 그러므로
실시간으로 검사규칙을 조정하기 위한 자동화된
시스템을 허용한다.
Port
Mirroring
BlackDiamond
12804C 는 manyto-one 과 cross module port mirroring 을 지원한다.
이것은
네트워크 공격에 대응할때 진단툴로써 경향분석이나 네트워크 관리자에
의해 활용되기 위한 침입탐지 장치와 같은 외부네트워크
장비를
위한 mirror traffic 에 이용될수있다.
Line-Rate
Access Control Lists
ACLs
는 네트워크 자원활용 제어와 네트워크 보안및 방어를 하기위한 가장
강력한 도구중의 하나이다.
BlackDiamond
12804C 는 Layer 2, 3 나 MAC address 혹은 IP source/destination address
와 같은 4-header information 에 기반한
수천개의 ACLs 를 지원한다.
Layer
3 Virtual Switching
Layer
3 가상스위칭으로, BlackDiamond 12804C 는 multi-layer switching 을
위한 가상화의 개념을 가져온다.
Layer
3 가상스위칭은 단일 스위치를 다수 가상라우터로 분할을 허용한다.
Layer
3 가상스위치는 물리적 라우터가 하는것과 같은 능력과 property(매개변수)를
가지고있다.
환경설정,
운영, 문제해결을 위한 모든 같은 라우팅 메카니즘을 상속한다.
이
결과로써, 각각 가상스위치 도메인은 분리된 관리와 안전한 보안을 위해
고립될수도 있다.
네트워크
트래픽은 보안위협을 최소화 하기위해 분리된 가상 도메인으로 격리될수있다.
각기
가상스위치를 위한 분리된 라우터 테이블은 라우터 분리를 가능하게한다.
Layer
3 가상스위칭은 운영자가 overlapping IP 주소공간을 이용할수있게 해주며
단일 물리적 네트워킹 인프라를 공유하기위해
다수
커뮤니티를 지원한다.
Hardened
Network Infrastructure
Denial
of Service Protection
BlackDiamond
12804C 는 DOS 공격을 훌륭히 다룬다.
만약
스위치가 CPU 입력 대기열에서 비정상적으로 많은 패킷을 탐지한다면,
CPU 도달로부터 이들패킷을 자동으로 멈추는 ACLs를
소집할
것이다. 얼마후에,
ACLs는 삭제되며 공격이 계속된다면, 다시 설치된다.
ASIC-based
Longest Prefix Match
Longest
Prefix Match (LPM) routing 은 새로운 흐름을 배우기위한 control plane
소프트웨어의 필요성을 경감시키며
네트워크가
DoS 공격에 탄력적으로 된다.
LPM
으로 인하여 CPU는 어떠한 인식되지않은 목적지를 향한 first packet
전송에 부담을 가지지 않으며,
중대업무를
위해 CPU를 자유롭게 한다.
Secure
Management
SSH2,
SCP ,SNMPv3 와 같은 프로토콜의 이용은 BlackDiamond 12804C 스위치가
관리운용의 방해와 man-in-the-middle
공격을 예방한다.
MD5
Authentication of Routing Protocols
라우팅
프로토콜의 MD5 승인은 공격자가 유효메시지 변경과 라우팅 세션 공격을
하지못하게 한다.
Automated
Attack Mitigation
- 감염된
source 네트워크로 들어감.
- BlackDiamond
12804C static ACLs 와 CLEAR-Flow rules DoS 공격을 걸러내며 수상한
트래픽으로 간주함.
- 심층분석을
위해 Sentriant 로 Selectively port-mirror traffic 을 보냄
- Sentriant
는 수상한 트래픽 감시를 계속하며 수상한 것으로부터 위험수준까지
트래픽 등급을 단계적으로 확대하기 위해 내부 규정을
이용한다.
- Sentriant
는 BlackDiamond 12804C 에서 dynamic ACL 을 시작한다.
- BlackDiamond
12804C 는 실시간으로 dynamic ACL 을 적용하며 수상한 트래픽 port
mirror 를 계속한다.
- Sentriant
는 또한 Extreme Networks EPICenter 네트워크 관리 소프트웨어로 mitigation
action(완화작용) 을 보낸다.
- EPICenter
는 보안정책(mitigation action) 강화를 위해 중앙과 하단스위치와 작동한다.
Target
Applications
Enterprise
Core
BlackDiamond
12804C 는 네트워크 필요성을 완벽하게 만족시키는 이상적인 백본스위치
솔루션을 중·소기업에 제공한다.
BlackDiamond
12804C 의 CLEARFlow Security Rules Engine 과 Layer 3 가상스위칭
능력은 백본 보안을 강화한다.
ExtremeXOS
에서 제공하는 확장성은 기업백본이 best-in-class security product
로 강하게 통합되도록 한다.
Traditional
Aggregation Layer
Extreme
네트워크는 two-tier 네트워크가 더 간편한 접근이라고 믿는 반면에,
building 이나 campus wiring plan 의 레이아웃은 가끔 집합
레이어를
필요로한다. 이
레이어는 전형적으로 하단스위치로 부터 기가비트나 10기가비트 업링크를
통합하며, 기가비트와 10기가비트
업링크를 통하여 중앙까지 연결한다.
BlackDiamond
12804C 는 고수행과 집합 레이어를 위해 요구되는 fault-tolerance(무정지형)
연결성을 위한 필요성을 보여준다.
Technical Specifications
ExtremeXOS 11.6 Supported Protocols
|
Switching
- RFC 3619 Ethernet Automatic Protection Switching (EAPS) and EAPSv2
- IEEE 802.1D - 1998 Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
- IEEE 802.1D - 2004 Spanning Tree Protocol (STP and RSTP)
- IEEE 802.1w - 2001 Rapid Reconfiguration for STP, RSTP
- IEEE 802.1Q-2003 (formerly IEEE 802.1s) Multiple Instances of STP, MSTP
- EMISTP, Extreme Multiple Instances of Spanning Tree Protocol
- PVST+, Per VLAN STP (802.1Q interoperable)
- Extreme Standby Router Protocol (ESRP)
- IEEE 802.1Q - 1998 Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks
- IEEE 802.3ad Static load sharing configuration and LACP based dynamic configuration
- IEEE 802.1AB - LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol
- LLDP Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED), ANSI/TIA-1057, draft 08
- Extreme Discovery Protocol (EDP)
- Extreme Loop Recovery Protocol (ELRP)
- Extreme Link State Monitoring (ELSM)
- Software Redundant Ports
VLANs, vMANs + MAC-in-MAC
- IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Tagging
- IEEE 802.1v: VLAN classification by Protocol and Port
- Port-based VLANs
- Protocol-based VLANs
- Multiple STP domains per VLAN
- IEEE 802.1ad Virtual MANs (vMANs)
- IEEE 802.1ah/D1.2 MAC-in-MAC Provider Bridging
Quality of Service and Policies
- IEEE 802.1D - 1998 (802.1p) Packet Priority
- RFC 2474 DiffServ Precedence, including 8 queues/port
- RFC 2598 DiffServ Expedited Forwarding (EF)
- RFC 2597 DiffServ Assured Forwarding (AF)
- RFC 2475 DiffServ Core and Edge Router Functions
IPv4
- RFC 1812 Requirements for IP Version 4 Routers
- RFC 1519 CIDR
- RFC 1256 IPv4 ICMP Router Discovery (IRDP)
- RFC 1122 Host Requirements
- RFC 768 UDP
- RFC 791 IP
- RFC 792 ICMP
- RFC 793 TCP
- RFC 826 ARP
- RFC 894 IP over Ethernet
- RFC 1027 Proxy ARP
- RFC 2068 HTTP server ??Used for web-based Network Login
- RFC 2338 VRRP
- Static Unicast Routes
- Static Multicast Routes
- RFC 1058 RIP v1
- RFC 2453 RIP v2
- RFC 2328 OSPF v2 (including MD5 authentication)
- RFC 1587 OSPF NSSA Option
- RFC 1765 OSPF Database Overflow
- RFC 2370 OSPF Opaque LSA Option
- RFC 3623 OSPF Graceful Restart
- RFC 1112 IGMP v1
- RFC 2236 IGMP v2
- RFC 3376 IGMP v3
- IGMP v1/v2/v3 Snooping with Configurable Router Registration Forwarding
- IGMP Filters
- Static IGMP Membership
- Multicast VLAN Registration
- RFC 2362 PIM-SM
- RFC 3569, draft-ietf-ssm-arch-06.txt PIM-SSM PIM Source Specific Multicast
IPv6
- RFC 2460, Internet Protocol, Version 6 (IPv6) Specification
- RFC 2461, Neighbor Discovery for IP Version 6, (IPv6)
- RFC 2462, IPv6 Stateless Address Auto configuration - Router Requirements
- RFC 2463, Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMPv6) for the IPv6 Specification
- RFC 2464, Transmission of IPv6 Packets over Ethernet Networks
- RFC 2465, IPv6 MIB, General Group and Textual Conventions
- RFC 2466, MIB for ICMPv6
- RFC 1981, Path MTU Discovery for IPv6, August 1996 - Router requirements
- RFC 3513, Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) Addressing Architecture
- RFC 3587, Global Unicast Address Format
- RFC 2710, IPv6 Multicast Listener Discovery v1 (MLDv1) Protocol
- RFC 3810, IPv6 Multicast Listener Discovery v2 (MLDv2) Protocol
- RFC 2080, RIPng
- RFC 2893, Configured Tunnels
- RFC 3056, 6to4
- Static Unicast routes for IPv6
- Telnet server over IPv6 transport
- SSH-2 server over IPv6 transport
- Ping over IPv6 transport
- Traceroute over IPv6 transport
Management and Traffic Analysis
- RFC 2030 SNTP, Simple Network Time Protocol v4
- RFC 854 Telnet client and server
- RFC 783 TFTP Protocol (revision 2)
- RFC 951, 1542 BootP
- RFC 2131 BOOTP/DHCP relay agent and DHCP server
- RFC 1591 DNS (client operation)
- RFC 1155 Structure of Mgmt Information (SMIv1)
- RFC 1157 SNMPv1
- RFC 1212, RFC 1213, RFC 1215 MIB-II, Ethernet-Like MIB & TRAPs
- RFC 1573 Evolution of Interface
- RFC 1650 Ethernet-Like MIB (update of RFC 1213 for SNMPv2)
- RFC 1901 - 1908 SNMP v2c, SMIv2 and Revised MIB-II
- RFC 2570 - 2575 SNMPv3, user based security, encryption and authentication
- RFC 2576 Coexistence between SNMP Version 1, Version 2 and Version 3
- RFC 1757 RMON 4 groups: Stats, History, Alarms and Events
- RFC 2021 RMON2 (probe configuration)
- RFC 2668 802.3 MAU MIB
- RFC 1643 Ethernet MIB
- RFC 1493 Bridge MIB
- RFC 1354 IPv4 Forwarding Table MIB
- RFC 2737 Entity MIB v2
- RFC 2233 Interface MIB
- RFC 3621 PoE-MIB (BlackDiamond 8800 only)
- RFC 1354 IP Forwarding Table MIB
- RFC 1724 RIPv2 MIB
- RFC 1850 OSPFv2 MIB
- RFC 1657 BGP-4 MIB
- Draft-ietf-idr-bgp4-mibv2-02.txt- ?Enhanced BGP-4 MIB
- draft-ietf-pim-mib-v2-o1.txt
- RFC 2787 VRRP MIB
- Draft-ietf-bridge-rstpmib-03.txt - Definitions of Managed Objects for Bridges
with Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
- Secure Shell (SSH-2) client and server
- Secure Copy (SCP-2) client and server
- Secure FTP (SFTP) server
- IEEE 802.1ag/D4.1 L2 Ping and traceroute
- sFlow version 5
- Configuration logging
- Multiple Images, Multiple Configs
- BSD System Logging Protocol (SYSLOG), with Multiple Syslog Servers
-999 Local Messages (criticals stored across reboots)
-
ExtremeWare vendor MIBs (includes FDB, PoE, CPU, Memory MIBs) http://www.extremenetworks.com/services/documentation
Security
- Routing protocol MD5 authentication (see above)
- Secure Shell (SSH-2), Secure Copy (SCP-2) and SFTP client/server with encryption/authentication
(requires export controlled encryption module)
- SNMPv3 user based security, with encryption/ authentication (see above)
- RFC 1492 TACACS+
- RFC 2138 RADIUS Authentication
- RFC 2139 RADIUS Accounting
- RFC 3579 RADIUS EAP support for 802.1x
- RADIUS Per-command Authentication
- Access Profiles on All Routing Protocols
- Access Policies for Telnet/SSH-2/SCP-2
- Network Login - 802.1x, web and MAC-based mechanisms
- IEEE 802.1x ??2001 Port-Based Network Access Control for Network Login
- Multiple supplicants with multiple VLANs for Network Login (all modes)
- Fallback to local authentication database (MAC and Web-based methods)
- Guest VLAN for 802.1x
- RFC 1866 HTML - Used for web-based Network Login
- SSL/TLS transport- ?used for for web-based Network Login, (requires export controlled
encryption module)
- MAC Security - Lockdown and Limit
- IP Security - RFC 3046 DHCP Option 82 with port and VLAN ID
- IP Security - DHCP enforcement via Disable ARP Learning
- IP Security - Gratuitous ARP Protection
- IP Security - Trusted DHCP Server
- IP Security - DHCP Secured ARP / ARP Validation
- Layer 2/3/4 Access Control Lists (ACLs)
- CLEAR-Flow, threshold based alerts and actions
Denial of Service Protection:
- RFC 2267 Network Ingress Filtering
- RPF (Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding) Control via ACLs
-
Wire-speed ACLs
- Rate Limiting / Shaping by ACLs
- IP Broadcast Forwarding Control
- ICMP and IP-Option Response Control
- SYN attack protection
- CPU DoS Protection with traffic rate-limiting to management CPU
- Robust against common Network Attacks:
- CERT (http://www.cert.org)
- CA-2003-04: "SQL Slammer"
- CA-2002-36: "SSHredder"
- CA-2002-03: SNMP vulnerabilities
- CA-98-13: tcp-denial-of-service
- CA-98.01: smurf
- CA-97.28:Teardrop_Land -Teardrop and "LAND" attack
- CA-96.26: ping
- CA-96.21: tcp_syn_flooding
- CA-96.01: UDP_service_denial
- CA-95.01: IP_Spoofing_Attacks_and_Hijacked_ Terminal_Connections
- IP Options Attack
|
-Teardrop, boink, opentear, jolt2, newtear, nestea, syndrop, smurf, fraggle, papasmurf,
synk4, raped, winfreeze, ping-f, ping of death, pepsi5, Latierra,
Winnuke, Simping, Sping, Ascend, Stream, Land, Octopus
Core Protocols: only available on switches with Core-License capability:
- PIM-DM Draft IETF PIM Dense Mode draft-ietfidmr-pim-dm-05.txt, draft-ietf-pim-dm-new-v2-04.
txt
- RFC 2740, OSPF for IPv6
- RFC 1771 Border Gateway Protocol 4
- RFC 1965 Autonomous System Confederations for BGP
- RFC 2796 BGP Route Reflection (supersedes RFC 1966)
- RFC 1997 BGP Communities Attribute
- RFC 1745 BGP4/IDRP for IP - OSPF Interaction
- RFC 2385 TCP MD5 Authentication for BGPv4
- RFC 2439 BGP Route Flap Damping
- RFC 2842 Capabilities Advertisement with BGP-4
- RFC 2918 Route Refresh Capability for BGP-4
- draft-ietf-idr-restart-10.txt Graceful Restart Mechanism for BGP
- EAPSv2 Shared Ports - multiple interconnections between rings
MPLS: requires MPLS Feature Pack license
- RFC 2205 Reservation Protocol
- RFC 2961 RSVP Refresh Overhead Reduction Extensions
- RFC 3031 Multiprotocol Label Switching Architecture
- RFC 3032 MPLS Label Stack Encoding
- RFC 3036 LDP
- RFC 3209 RSVP-TE: Extensions to RSVP for LSP Tunnels
- RFC 3630 Traffic Engineering Extensions to OSPFv2
- draft-ietf-l2vpn-vpls-ldp-08
- draft-ietf-pwe3-control-protocol-17
- draft-ietf-pwe3-ethernet-encap-11
- draft-ietf-mpls-lsp-ping-13
- RFC 3811 Definitions of Textual Conventions (TCs) for Multiprotocol Label Switching
(MPLS) Management
- RFC 3812 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Traffic Engineering (TE) Management
Information Base (MIB)
- RFC 3813 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Label Switching Router (LSR) Management
Information Base (MIB)
- RFC 3815 Definitions of Managed Objects for the Multiprotocol Label Switching
(MPLS), Label Distribution Protocol (LDP)
- draft-ietf-pwe3-pw-mib-06
- draft-ietf-pwe3-pw-mpls-mib-07
- draft-ietf-pwe3-enet-mib-06
General Specifications
Switching Capacity
MSM and I/O Modules
- MSM-5: MSM modules contain both the control plane as well as the switch fabric
for the BlackDiamond 12804.
- GM-20XT: 20-port Gigabit Ethernet module. Each port can be used for 10/100/1000BASET
or mini-GBIC connectivity (requires mini-GBIC modules)
- GM-20T: 20-port 10/100/1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet module (RJ-45)
- XM-2X: 2-port 10G module. XENPAK modules required.
Power Supply Options
Both AC and DC power supplies are available
-
AC power supplies can run from 90-264 VAC, and deliver
-700W at 90V to 120V, or
-1200W at 200V to 240V
-
48V DC power supplies deliver 1200W of power
Physical Specifications
Dimensions
- Chassis: 17.5" high x 17.51" wide x 18.23??deep (44.45 cm x 44.5 cm
x 46.3 cm)
- MSM Module Dimensions: 1.63 "high x 15.26" wide x 15.25" deep
(4.1 cm x 38.8 cm x 38.7 cm)
- I/O Module Dimensions: 1.63??high x 15.26 "wide 15.25" deep (4.1 cm
x 38.8 cm x 38.7 cm)
Weight
- Empty Chassis: 65 lb (29.5 kg)
- Power Supply: 7 lb (3.2 kg)
- MSM-5 8.5 lb (3.9 kg)
- G20XT 8.5 lb (3.9 kg)
- G20T 7.5 lb (3.4 kg)
- XM-2X 7 lb (3.2 kg)
Power
- Chassis with Fan Trays: 45W, 48V, 1.0A (Heat Dissipation: 154 BTU)
- MSM-5: 185W, 48V, 3.3A (Heat Dissipation: 632 BTU)
- GM-20XT Module: 161W, 48V, 3.5A (Heat Dissipation: 549 BTU)
- GM-20T Module: 149W, 48V, 3.5A (Heat Dissipation: 509 BTU)
- XM-2X Module: 132W, 48V, 2.9A (Heat Dissipation: 450 BTU)
Regulatory/Safety Standards
North American Safety of ITE
- UL 60950-1:2003 1st Ed., Listed Device (U.S.)
- CSA 22.2#60950-1-03 1st Ed.(Canada)
- Complies with FCC 21CFR Chapter1, Subchapter J (U.S. Laser Safety)
- CDRH Letter of Approval (U.S. FDA Approval)
- IEEE 802.3af 6-2003 Environment A for PoE Applications
European Safety of ITE
- EN60950-1:2001
- EN 60825-1+A2:2001 (Lasers Safety)
- TUV-R GS Mark by German Notified Body
- 73/23/EEC Low Voltage Directive
International Safety of ITE
- CB Report & Certificate per IEC 609501:2001+All Country Deviations
- AS/NZX 3260 (Australia/New Zealand)
EMI/EMC Standards
North America EMC for ITE
- FCC CFR 47 part 15 Class A (USA)
- ICES-003 Class A (Canada)
- European EMC standards
- EN 55022:1998 Class A
- EN 55024:1998 Class A
- includes IEC 61000-4-2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 11
- EN 61000-3-2,3 (Harmonics & Flicker)
- ETSI EN 300 386:2001 (EMC Telecommunications)
- 89/336/EEC EMC Directive
International EMC Certifications
- CISPR 22:1997 Class A (International Emissions)
- CISPR 24:1997 Class A (International Immunity)
- IEC/EN 61000-4-2 Electrostatic Discharge, 8kV Contact, 15kV Air, Criteria A
- IEC/EN 61000-4-3 Radiated Immunity 10V/m, Criteria A
- IEC/EN 61000-4-4 Transient Burst, 1kV, Criteria A
- IEC/EN 61000-4-5 Surge, 2kV, 4kV, Criteria A
- IEC/EN 61000-4-6 Conducted Immunity, 0.1580MHz, 10V/m unmod. RMS, Criteria A
- IEC/EN 61000-4-11 Power Dips & Interruptions, >30%, 25 periods, Criteria
C
Country Specific
- VCCI Class A (Japan Emissions)
- AS/NZS 3548 ACA (Australia Emissions)
- CNS 13438:1997 Class A (BSMI-Taiwan)
- NOM/NYCE (Mexico)
- MIC Mark, EMC Approval (Korea)
Environmental
- EN/ETSI 300 019-2-1 v2.1.2 ??Class 1.2 Storage
- EN/ETSI 300 019-2-2 v2.1.2 ??Class 2.3 Transportation
- EN/ETSI 300 019-2-3 v2.1.2 ??Class 3.1e Operational
- EN/ETSI 300 753 (1997-10) ??Acoustic Noise
- NEBS GR-63 Issue 2 ??Sound Pressure
- ASTM D3580 Random Vibration Unpackaged 1.5G
Warranty
- 1-year on Hardware
- 90-days on Software
|
|



